The Autonomous Database on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) is revolutionising how businesses manage their data, offering unprecedented automation, scalability, and security.
Oracle Autonomous Database is a cloud-based service that automates tasks like provisioning, configuring, tuning, and scaling using advanced machine learning. It minimizes human intervention, reduces errors, lowers operational costs, and boosts performance, allowing organizations to focus on strategic goals. With built-in AI and support for LLMs, it accelerates app innovation, enabling natural language queries, contextual conversations, and retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) through its vector store. Integrated AI and in-database ML enhance applications with text, image, and speech analysis, along with personalized recommendations.
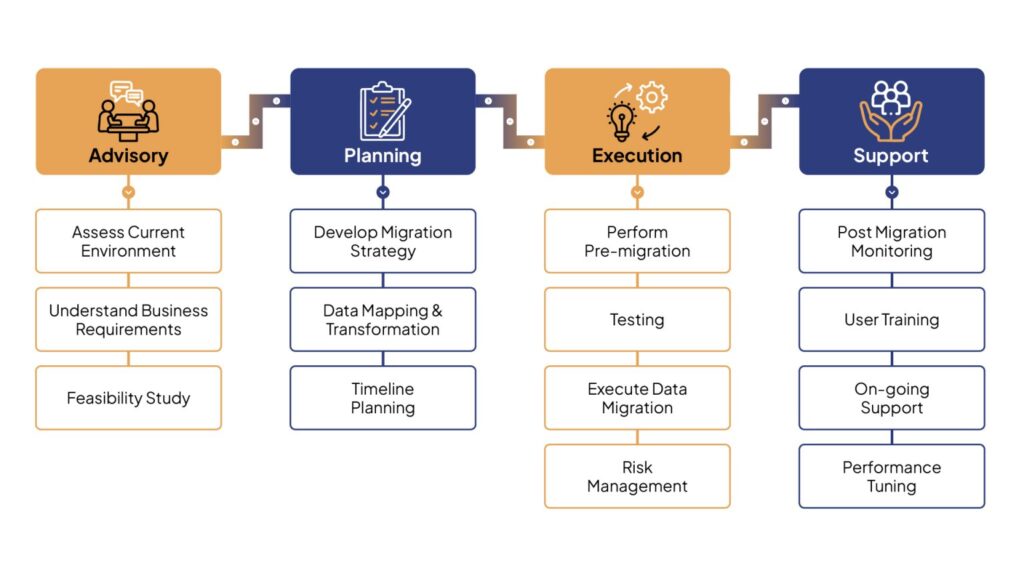
Key Features of Oracle Autonomous Database
- Self-Driving Capabilities: One of the significant features of the Autonomous Database is its self-driving capabilities. It automatically provisions resources, tunes performance, and applies security patches, ensuring optimal database performance without manual intervention.
- Self-Securing: Security is paramount today. The Autonomous Database automatically protects against unauthorised access and cyber threats by applying security updates and patches in real-time. This reduces the risk of vulnerabilities and enhances data integrity.
- Self-Repairing: The Autonomous Database minimises downtime through its self-repairing capabilities. It automatically detects and resolves issues, ensuring high availability and reliability.
- Scalability: With OCI’s flexible infrastructure, the Autonomous Database can easily scale resources up or down based on demand. This elasticity allows organisations to efficiently manage workloads without over-provisioning or underutilising resources.
- Support for Multiple Workloads: The Autonomous Database supports both transactional (OLTP) and analytical (OLAP) workloads, making it suitable for a wide range of applications, from online transaction processing to data warehousing, as well as JSON workloads, through specialized configurations like Autonomous Transaction Processing (ATP) for transactions and Autonomous Data Warehouse (ADW) for analytics.
- Integration with Machine Learning: By integrating machine learning capabilities, the Autonomous Database enables organisations to perform advanced analytics and predictive modelling directly within the database. This empowers businesses to derive deeper insights from their data.
Benefits of Oracle Autonomous Database
- Cost Efficiency: Automating routine database management tasks reduces the need for extensive IT resources, leading to significant cost savings. Organisations can allocate their budget strategically, investing in innovation rather than maintenance.
- Improved Performance: The self-tuning capabilities of the Autonomous Database ensure that performance is optimised continuously. This leads to faster query response times and improves overall application performance.
- Enhanced Security: With automatic updates and real-time threat detection, organisations can rest assured that their data is secure. This built-in security reduces the risk of breaches and compliance violations.
- Faster Time to Market: By eliminating the complexities of database management, organisations can focus on developing and deploying applications more quickly. This agility allows businesses to respond to market changes and customer needs more effectively.
- Seamless Integration with OCI: The Autonomous Database is designed to work seamlessly within the OCI ecosystem. Organizations can easily integrate it with other Oracle services, such as Oracle Analytics Cloud and Oracle Data Science, to create comprehensive data solutions.
Use Cases for Oracle Autonomous Database
- Data Warehousing: Organisations can leverage the Autonomous Database for data warehousing, enabling them to store and analyse large volumes of data. Its ability to handle complex queries and analytics makes it ideal for business intelligence applications.
- Application Development: Developers can utilise the Autonomous Database as a backend for applications, benefiting from its scalability and performance. This allows for rapid development and deployment of applications that require robust data management.
- Financial Services: In the financial sector, the Autonomous Database can streamline operations by automating compliance reporting, transaction processing, and risk management. Its security features also help mitigate fraud and data breaches.
- Healthcare: Healthcare organisations can use the Autonomous Database to manage patient data, improve research outcomes, and enhance operational efficiency. The database’s self-securing capabilities ensure compliance with regulations like HIPAA.
- E-commerce: E-commerce businesses can benefit from the Autonomous Database’s ability to handle fluctuating workloads during peak shopping seasons. Its performance and scalability ensure that online platforms can provide a seamless customer experience.
- Transactional Workloads: Supports online transaction processing (OLTP) with high scalability and low latency, enabling real-time fraud detection through advanced machine learning algorithms for enhanced security and seamless user experiences.
- JSON-Based Applications: Enable native storage, querying, and analysis of JSON data, offering NoSQL-like features to support modern app development with enhanced flexibility, scalability, and efficient data handling.
- Backup and Disaster Recovery: Ensure automated backups and replication for high availability, coupled with robust disaster recovery strategies to minimize downtime and maintain business continuity.
Conclusion
Eliminate database complexities with Yotta’s comprehensive Oracle Solutions and Managed Services. Our expert team ensures end-to-end management, security, seamless implementation, and high availability for your business-critical databases. Whether you are migrating from an on-premises data center to the cloud, or moving data between different cloud environments, Yotta’s Oracle Migration Services guarantee a smooth transition with zero disruption to your business operations.
With specialised services like cloud migration, platform migration, and continuous updates, we make sure your database is always optimised for performance and security. Yotta’s provide Oracle services in a Tier-4 Fault-Tolerant Data Center (DC-NM1), for maximum uptime and reliability or your Location. Additionally, we offer consulting and resource augmentation to support your team at every stage of the migration process.
By automating routine tasks and providing advanced analytics capabilities, the Autonomous Database enables businesses to focus on innovation and strategic growth. As organisations continue to navigate the complexities of data management, embracing solutions like the Oracle Autonomous Database will be crucial in staying competitive in an increasingly data-driven landscape.